TOP CATEGORY: Chemicals & Materials | Life Sciences | Banking & Finance | ICT Media
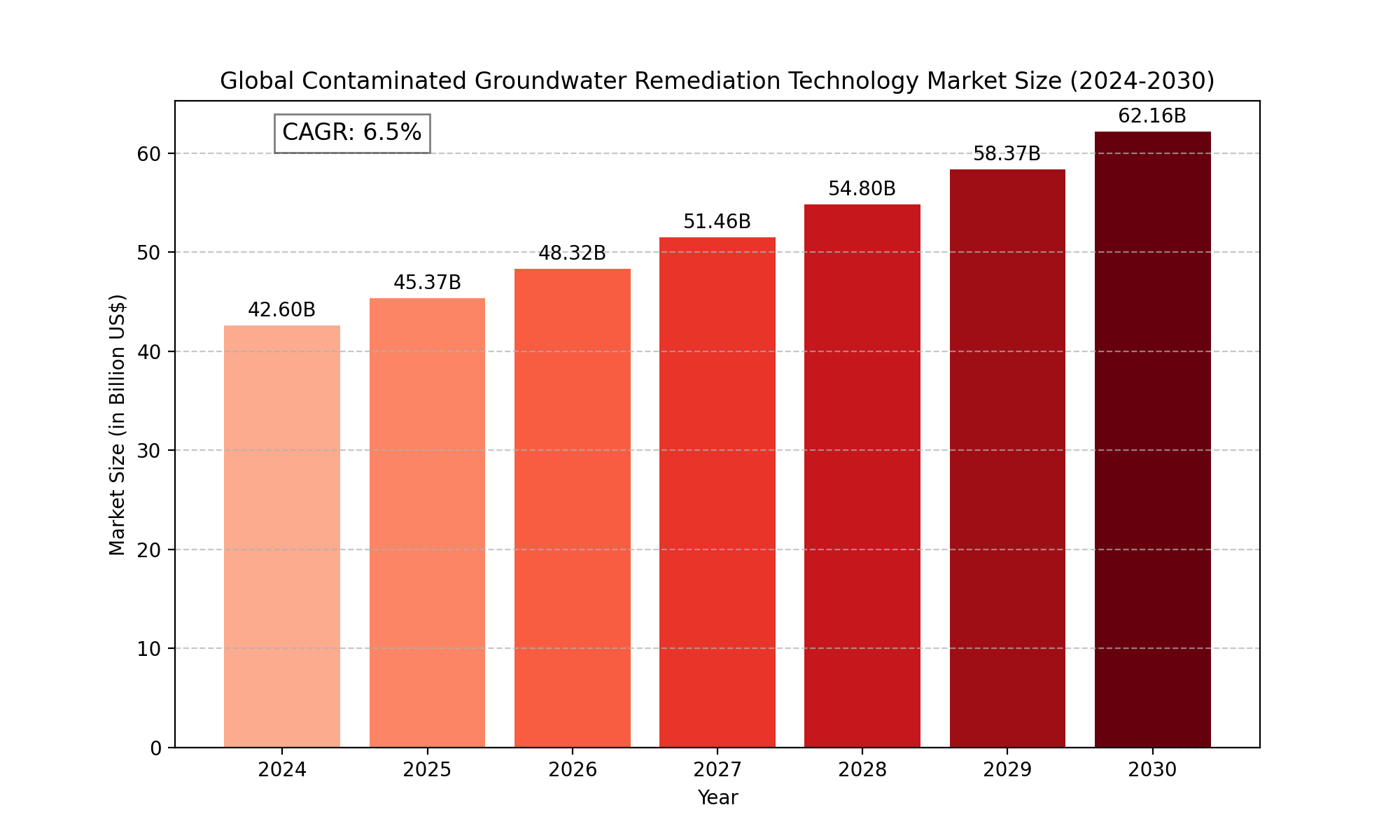
The "Global Contaminated Groundwater Remediation Technology Market" size was valued at US$ 42.6 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US$ 62.16 Billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.5% during the forecast period 2024-2030.
Contaminated Groundwater Remediation Technology refers to the methods, processes, and equipment used to remove, degrade, or contain pollutants in groundwater, restoring it to a safe condition for human use and environmental health. This includes physical, chemical, and biological treatment techniques applied in-situ or ex-situ.
The global Contaminated Groundwater Remediation Technology market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing water scarcity concerns, stricter environmental regulations, and the persistent challenge of legacy contamination sites. In 2023, in-situ remediation technologies accounted for 58% of the market value, with pump-and-treat systems still widely used but losing market share to more innovative approaches.
The growing need to manage water pollution and environmental deterioration brought on by industrial operations, agricultural runoff, and urbanisation is driving the global market for contaminated groundwater treatment technologies. Because of the serious threats that groundwater contamination poses to ecosystems, human health, and water sources, governments and businesses everywhere are implementing remediation solutions. These technologies include biological processes like bioremediation, chemical treatments like in-situ oxidation, and physical techniques like pump-and-treat to eliminate or neutralise dangerous pollutants.
Stricter environmental laws and growing public awareness of sustainable water management techniques are driving market expansion. Key end users of remediation methods include industries that contribute significantly to groundwater contamination, including manufacturing, mining, oil and gas, and chemicals. The increasing occurrence of contaminants that need specific treatments, such as heavy metals, organic chemicals, and PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), is driving the need for improved remediation methods. Although the industry is confronted with obstacles like as exorbitant expenses and intricate pollution specific to a given site, developments in remediation technologies, including in-situ and bio-based approaches, are opening up new growth prospects.

In terms of Remediation Technology, Global Contaminated Groundwater Remediation Technology has been segmented as Physical & Chemical Treatment, Biological Treatment, Thermal Treatment, and Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA).
Physical and chemical treatment have the highest market shares in the global market for contaminated groundwater remediation technologies. This section covers popular methods that work well for dealing with a variety of pollutants, such as hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as pump-and-treat, air sparging, chemical oxidation, and ion exchange.
In comparison to other technologies, physical and chemical processes are favoured due to their adaptability, efficiency, and speed of results. They are especially utilised in industrial settings with high pollution levels where prompt treatment is necessary to stop additional environmental harm. Furthermore, these techniques can be used in a variety of contamination circumstances, such as groundwater tainted by oil spills, industrial waste, and agricultural runoff. The physical and chemical treatment segment continues to dominate due to its effectiveness, broad applicability, and regulatory acceptance in high-risk sites, even though biological treatment and thermal treatment are becoming more popular, especially for certain contaminants, and monitored natural attenuation (MNA) is a passive, cost-effective method frequently used for less severe contamination.
Ex Suit to hold the highest market share: By Remediation Technology
In terms of Remediation Technology, Global Contaminated Groundwater Remediation Technology has been segmented as In Situ Remediation, Ex Situ Remediation.
In the contaminated groundwater remediation technology market, ex situ remediation currently holds the largest market share. Using techniques like pump-and-treat, soil washing, or chemical treatment, ex situ remediation entails removing polluted groundwater or soil for surface or offsite treatment. Its efficacy in managing a variety of contaminants, including heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), has led to its widespread adoption, particularly in highly contaminated areas where prompt intervention is required.
Because it gives direct control over the treatment process, ex situ remediation is frequently preferred because it guarantees a higher degree of efficiency and dependability. For many industries, including chemical plants, refineries, and industrial waste sites, this approach has long been the preferred choice when handling complicated and dangerous contamination situations.
Due in significant part to strict environmental rules enforced by organisations such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, which upholds the Safe Drinking Water Act and the Clean Water Act, North America has the greatest market share. Groundwater in the area has long been contaminated by industrial and agricultural operations, especially in industries like manufacturing, chemicals, and oil and gas. The need for sophisticated clean-up technology has grown as a result of growing worries about new pollutants like PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds).The U.S. and Canada are leading adopters of both in situ and ex situ technologies, with robust investments in environmental sustainability.
December 20th, 2023, U.S. Water Utilities Deploy PFAS Treatment Technologies to Safeguard Drinking Water for Communities. As U.S. and European lawmakers tighten restrictions on toxic PFAS contaminants in water, utilities and businesses are working to safeguard drinking water supplies for communities
Growing Stringent Environmental Regulations
The market for groundwater contamination remediation technologies is mostly driven by the stricter environmental laws that are being enforced by governments and environmental organisations around the globe. Industries are being forced to address and clean up contaminated groundwater by laws like the U.S. Clean Water Act, the European Union's Water Framework Directive, and different national regulations in areas like Asia-Pacific. In industrialised nations like North America and Europe, where industries are required to clean up contaminated sites in order to meet environmental safety standards, avoid legal penalties, and preserve operating licenses, these rules are particularly stringent.
Industries are under more pressure to implement cutting-edge remediation technologies as a result of growing public awareness of the health risks connected to contaminated groundwater, including exposure to heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and newly discovered contaminants like PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances). Industries are concentrating more on sustainable water management and minimising their environmental impact as environmental concerns continue to rise. The need for creative and efficient groundwater remediation solutions is being driven by this regulatory push as well as CSR initiatives in a number of industries, including manufacturing, chemicals, oil and gas, and agriculture.
The increasing use of innovative and sustainable remediation technologies, especially in situ remediation techniques, is a noteworthy trend in the market for contaminated groundwater remediation technologies. Industries are moving towards technologies that reduce environmental impact while providing efficient contamination treatment in response to growing environmental concerns and the drive for more environmentally friendly solutions. In situ methods, like chemical oxidation, bioremediation, and phytoremediation, are becoming more popular since they eliminate the need for excavation and remediate pollutants on the spot, saving money and minimising environmental disturbance.
The development of cutting-edge technologies that provide more accuracy in addressing pollutants, such as electrokinetic remediation and Nano remediation, is another trend. In order to combat new pollutants like PFAS and other persistent organic contaminants that are difficult to eliminate using conventional techniques, these technologies are being developed. Furthermore, real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making are increasingly being integrated through digital technology, enabling more effective and customised remediation strategies.
The high cost of Remediation Processes is a major barrier to the market for contaminated groundwater remediation technologies. Because modern remediation technologies, especially ex situ approaches, need specialised equipment, a lot of labour, and extended treatment times, their implementation can be prohibitively expensive. Delays in resolving polluted sites may result from this cost burden discouraging businesses, particularly smaller ones or those operating in developing nations, from completing essential remediation operations.
Furthermore, because different pollutants may need different treatment techniques, the intricacy of contamination scenarios can present difficulties. Multiple pollutants can sometimes make the remediation procedure more difficult, resulting in longer turnaround times and higher expenses. Investment decisions may be further hampered by the lack of knowledge regarding the efficacy of specific remediation technologies in reaching targeted clean-up levels.
|
Attributes |
Details |
|
Segments |
By Remediation Technology:
By Contaminant Type:
By Application:
By Treatment Type:
By End-User:
|
|
Region Covered |
|
|
Key Market Players |
|
|
Report Coverage |
|